Results from the REPLACE (Riociguat rEplacing PDE-5i therapy evaLuated Against Continued PDE-5i thErapy) study in adult patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) who were receiving PDE5i therapy and still at intermediate risk1
PATENT-1 Study Design
PATENT-1: A CLINICAL STUDY DESIGNED TO EVALUATE CRITICAL ENDPOINTS2,3
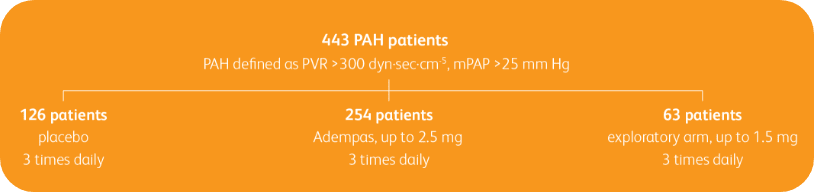
PIVOTAL TRIAL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH PAH (WHO GROUP 1)2,3
Randomized, double-blind, multinational, placebo-controlled, 12-week, phase 3 study2,3
Primary endpoint2,3
- Change in 6MWD from baseline to Week 12
Baseline characteristics2,3
- Mean age: 51 years (approximately 80% female)
- PAH etiologies: idiopathic (61%), familial (2%), associated with connective tissue disease (25%), congenital heart disease (8%), portal hypertension (3%), or anorexigen or amphetamine use (1%)
- Mean 6MWD was 363 m
- Concomitant medications: oral anticoagulants, diuretics, digitalis, calcium channel blockers, and oxygen were allowed
- Patient population was: 50% treatment naïve, 44% pretreated with an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA), and 6% pretreated with a prostacyclin analog (PCA)
- The majority of patients had WHO FC II (42%) or III (54%) at baseline
- Patients with systolic blood pressure <95 mm Hg were excluded
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; mPAP = mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance; WHO FC = World Health Organization Functional Class.
PATENT-1 Results
START WITH A TREATMENT THAT SHOWED EARLY IMPROVEMENT IN EXERCISE CAPACITY AND SIGNIFICANT RESULTS AT WEEK 122
Improvement in 6MWD was observed at 2 weeks and continued through 12 weeks2
SIGNIFICANT IMPROVEMENT IN 6MWD AT WEEK 122
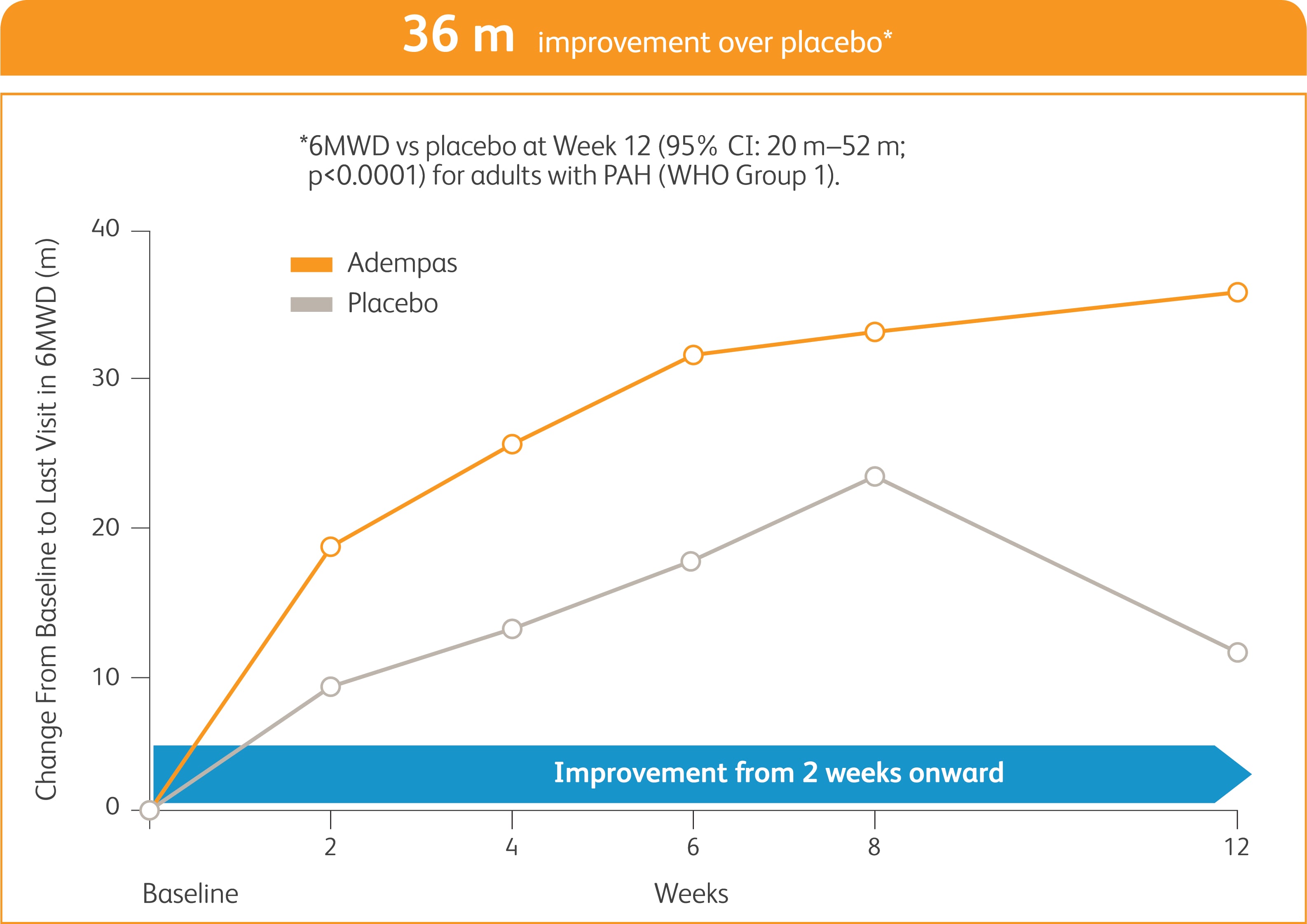
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance.
Adempas can be used as monotherapy or in combination
- In WHO FC II and III
- As monotherapy
- In combination with endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs)
- In combination with prostacyclin analogs (PCAs)
START WITH A TREATMENT THAT PROVIDED STRONG IMPROVEMENT IN WHO FC2
50% more patients improved WHO FC vs placebo2
CHANGE IN WHO FC IN THE 12-WEEK PATENT-1 STUDY2
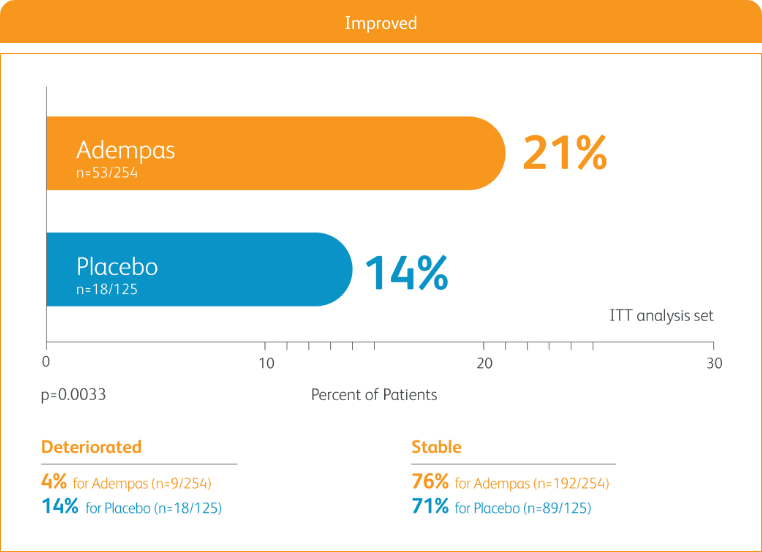
ITT = intention-to-treat
START WITH A TREATMENT THAT SIGNIFICANTLY DELAYED TIME TO CLINICAL WORSENING2†
Adempas significantly delayed time to clinical worsening2†
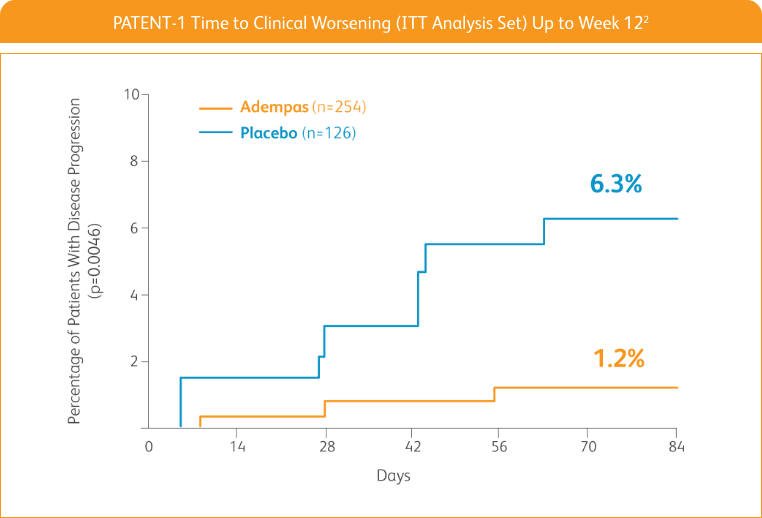
†Time to clinical worsening was a combined endpoint defined as death (all-cause mortality), heart/lung transplantation, atrial septostomy, hospitalization due to persistent worsening of pulmonary hypertension, start of new PAH-specific treatment, persistent decrease in 6MWD, and persistent worsening of WHO FC.
‡The Kaplan-Meier plot of time to clinical worsening is presented in the figure above. Patients treated with Adempas experienced a significant delay in time to clinical worsening vs placebo-treated patients (p=0.0046; stratified log-rank test). Significantly fewer events of clinical worsening up to Week 12 (last visit) were observed in patients treated with Adempas (1.2%) compared to placebo (6.3%) (p=0.0285, Mantel-Haenszel estimate).
START WITH A TREATMENT THAT DELIVERED STRONG IMPROVEMENTS IN PVR AND NT‑proBNP2,3‡
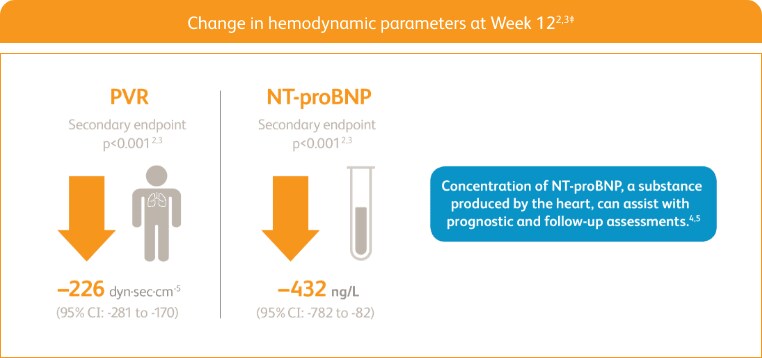
Right heart catheterization was performed at the beginning and end of the study period in 339 patients.
NT-proBNP = n-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance.
‡Placebo-adjusted mean change from baseline.
Results from the REPLACE (Riociguat rEplacing PDE-5i therapy evaLuated Against Continued PDE-5i thErapy) study in adult patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) who were receiving PDE5i therapy and still at intermediate risk1
TRANSITIONING TO ADEMPAS IN PATIENTS WITH PAH (WHO GROUP 1) WHO ARE ON TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i AND STILL AT INTERMEDIATE RISK1
Prospective, randomized, controlled, open-label, international, multicenter study to evaluate the efficacy of Adempas in adult patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) who are receiving a stable dose of a PDE5i and still at intermediate risk
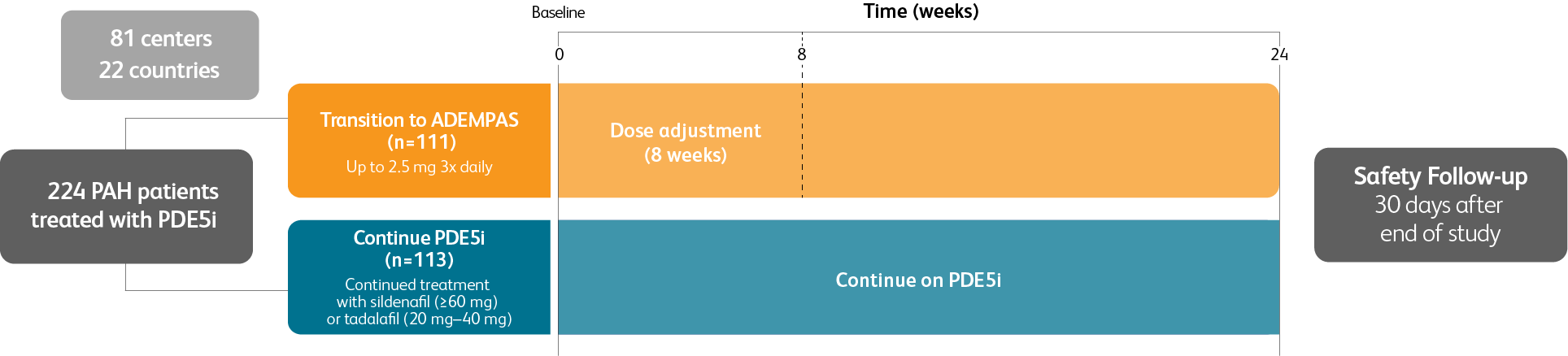
Patient population
Adult patients with PAH (WHO Group 1) receiving a stable dose of PDE5i with or without concomitant treatment with an ERA for ≥6 weeks and still at intermediate risk1
Intermediate risk defined as1:
- WHO FC III
- 6MWD 165 m–440 m
Baseline PDE5i monotherapy or combination therapy1
Primary endpoint
Composite endpoint of clinical improvement in the absence of clinical worsening at 24 weeks1
Clinical improvement at 24 weeks defined as1:
- Prespecified improvements in 2 out of 3 parameters1:
- Improvement in 6MWD of ≥10% or ≥30 m
- Improvement to WHO FC I or II
- Decrease in NT-proBNP ≥30%
- Absence of clinical worsening1
- Defined as death from any cause; hospitalization for worsening PAH (non-elective hospitalization due to PAH or initiation of parenteral prostanoid therapy); or disease progression (decrease in 6MWD ≥15% on two separate days plus either worsening WHO FC, need for new PAH-targeted medication, or decompensated right-sided heart failure)
Secondary endpoints, analyzed hierarchically1:
• Change in 6MWD
• Change in NT-proBNP
• Change in WHO FC
• Time to clinical worsening
Safety
- Adverse events (AEs) and other safety outcomes were evaluated throughout the study and at the 30-day safety follow-up1
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; ERA = endothelin receptor antagonist; NT-proBNP = n-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide; PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; WHO FC = World Health Organization Functional Class.
Composite primary endpoint
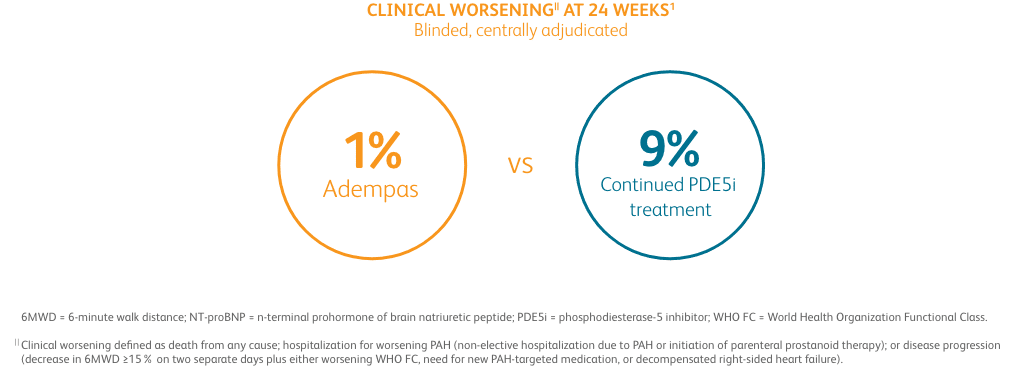
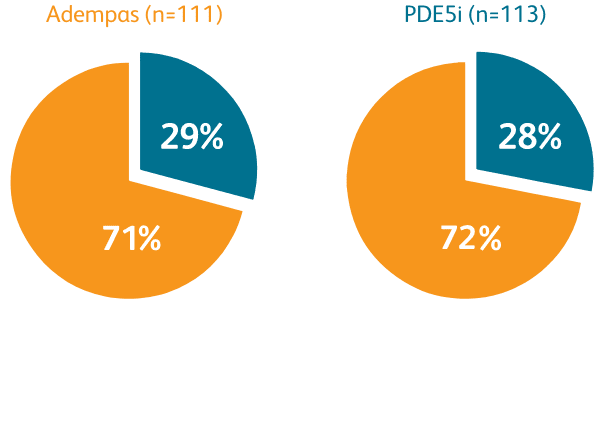
CLINICAL IMPROVEMENT§ IN INTERMEDIATE RISK PATIENTS WITH PAH (WHO GROUP 1) TRANSITIONING TO ADEMPAS VS CONTINUING PDE5i THERAPY1
§Clinical improvement at 24 weeks defined as prespecified improvements in 2 out of 3 parameters (6MWD, WHO FC, and/or NT-proBNP) and absence of clinical worsening1†
Clinical Improvement at 24 Weeks1
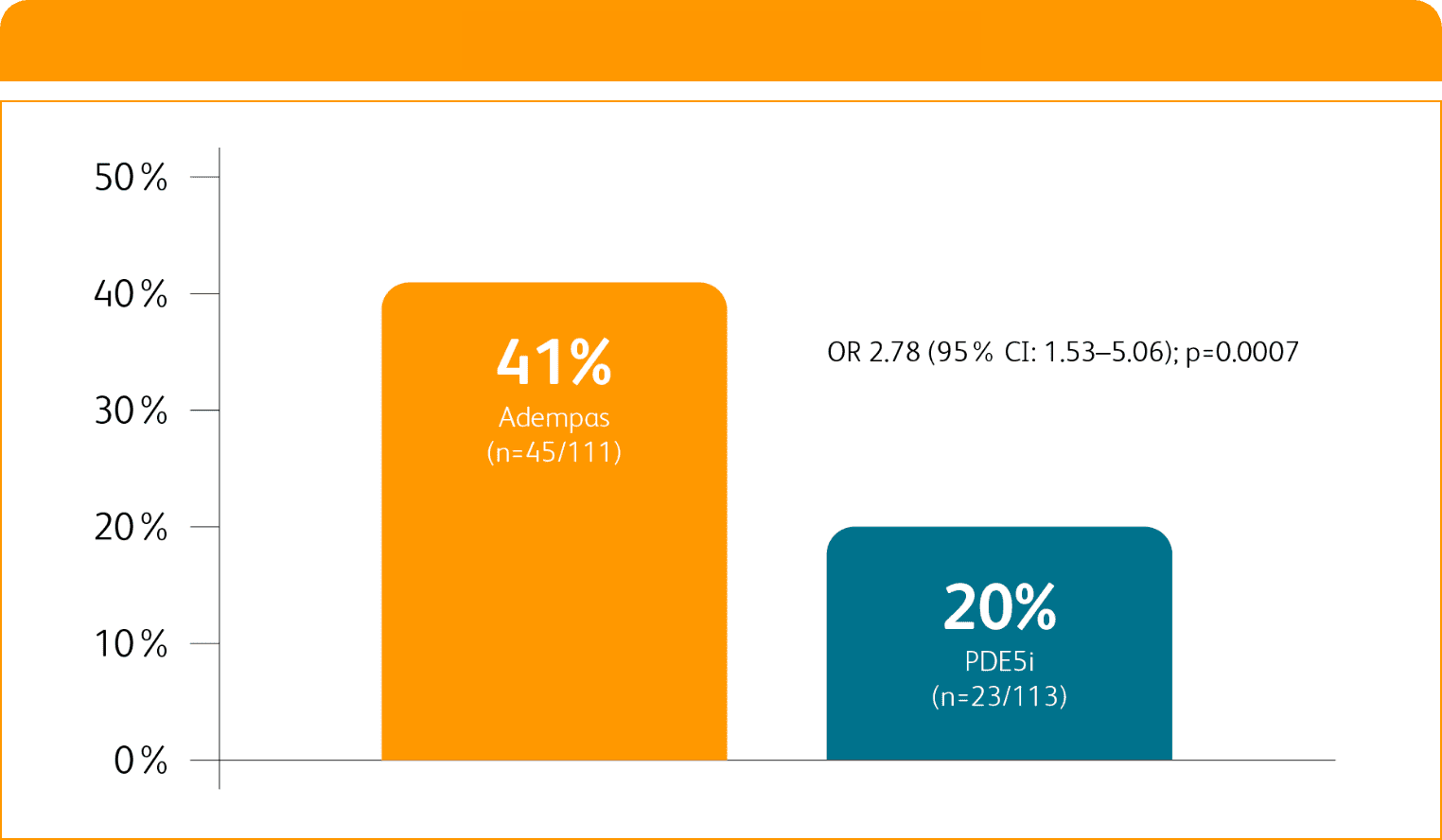
Per hierarchical testing procedures, these results are considered exploratory
CHANGE IN 6MWD ON ADEMPAS VS THOSE CONTINUING TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i1
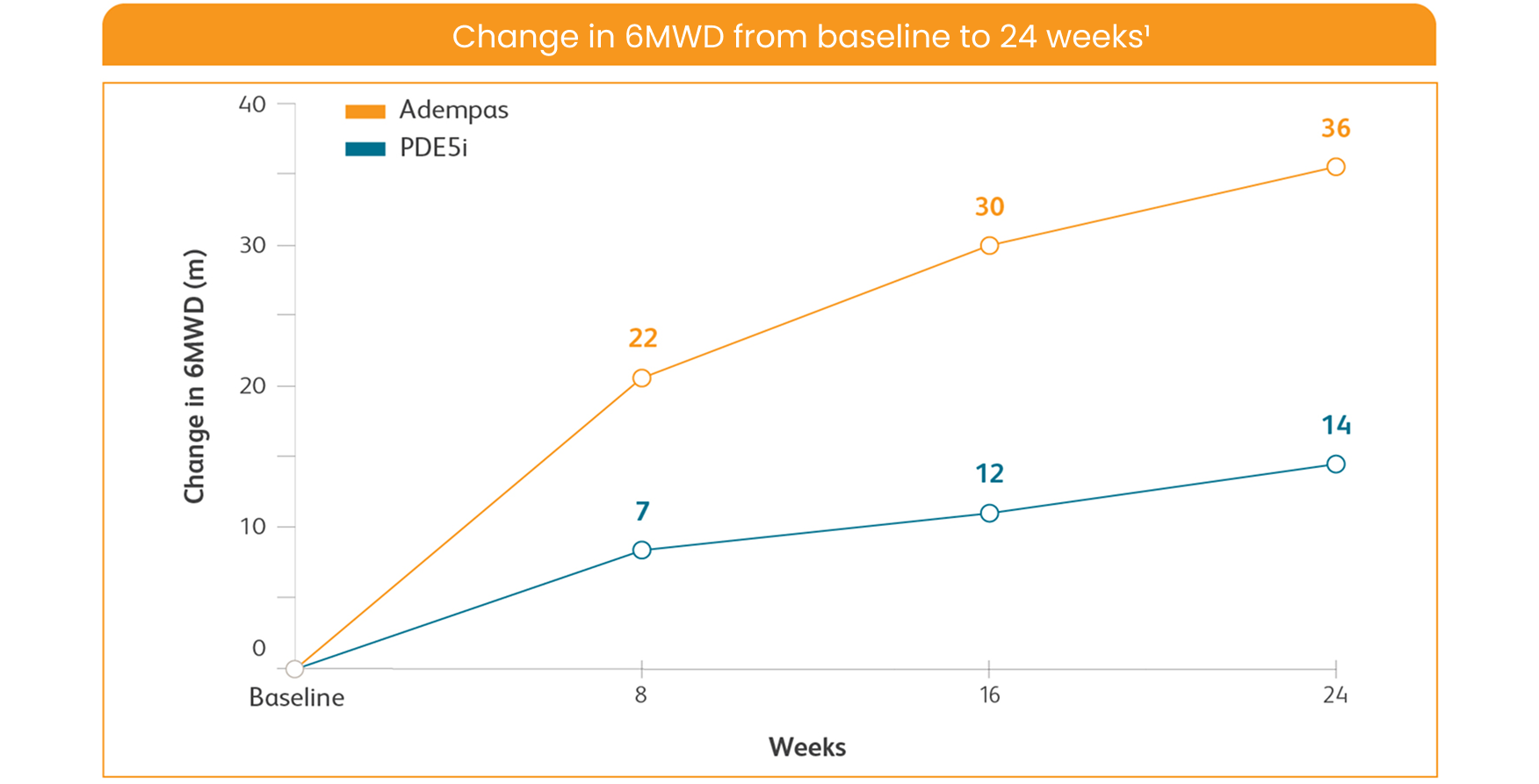
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor.
Per hierarchical testing procedures, these results are considered exploratory
CHANGE IN NT-proBNP ON ADEMPAS VS THOSE CONTINUING TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i1
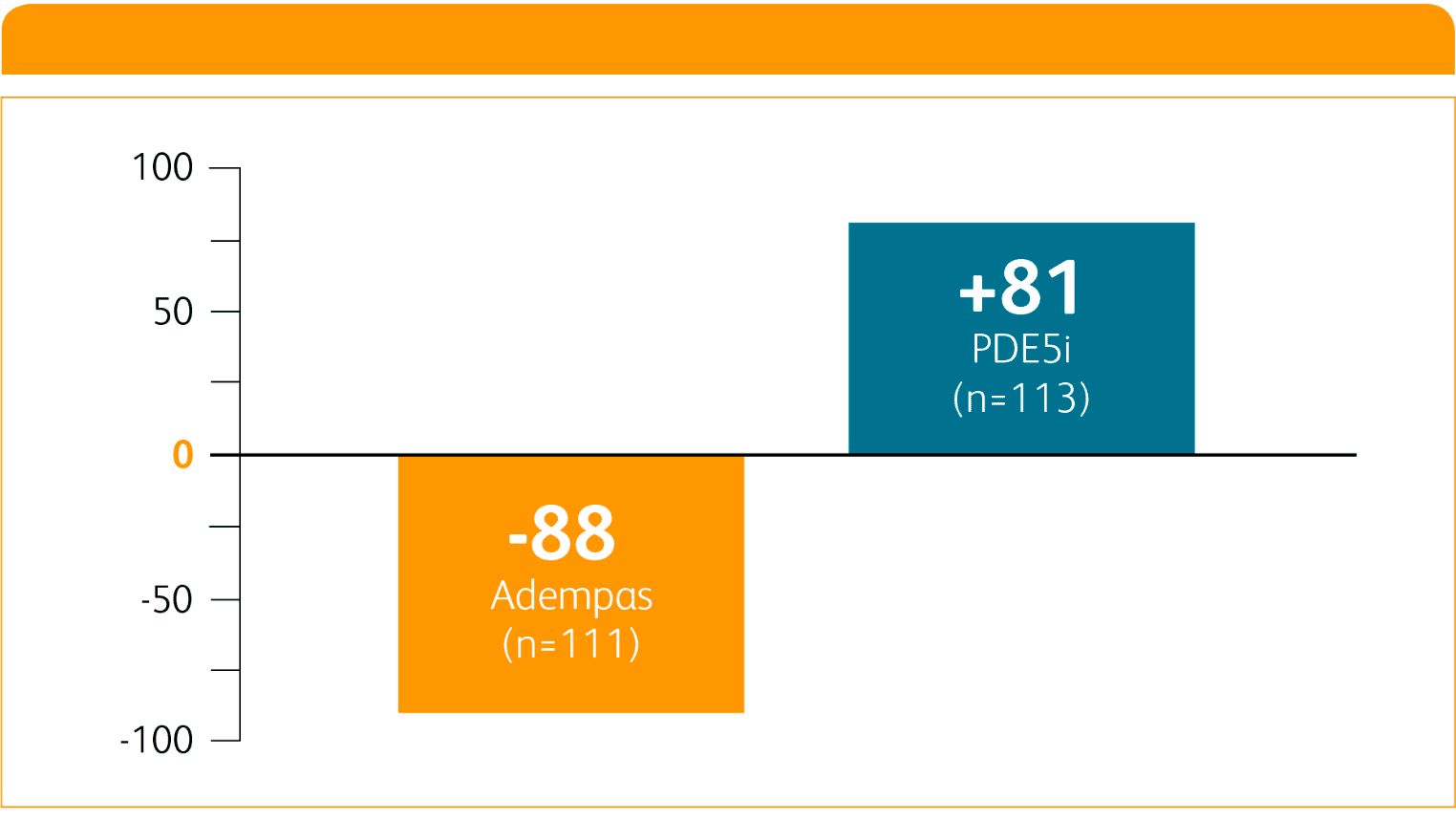
NT-proBNP = n-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide;
PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor.
Per hierarchical testing procedures, these results are considered exploratory
WHO FC ON ADEMPAS VS THOSE CONTINUING TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i1
WHO FC ON ADEMPAS VS THOSE
CONTINUING TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i1
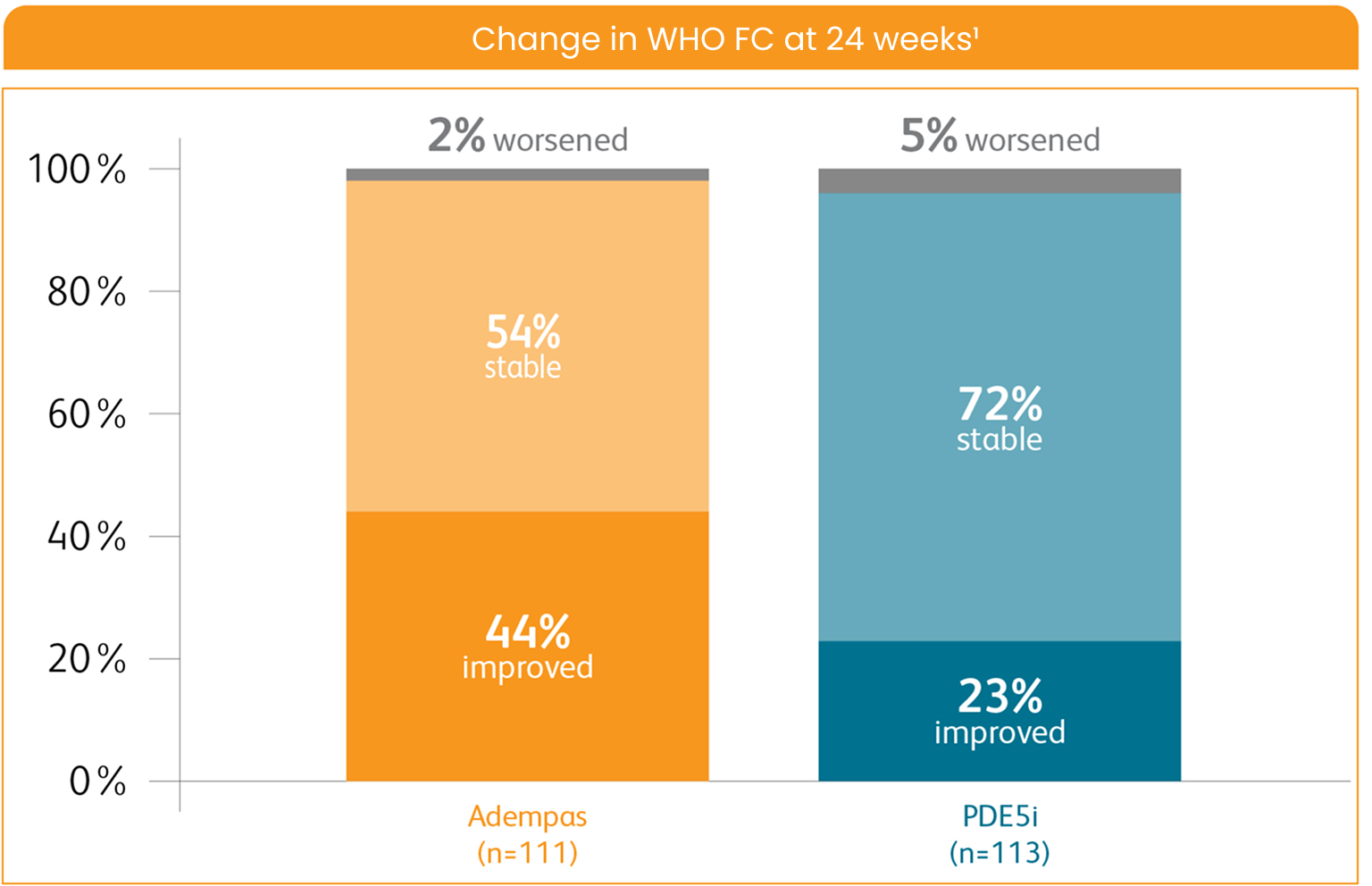
PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; WHO FC = World Health Organization Functional Class.
Per hierarchical testing procedures, these results are considered exploratory
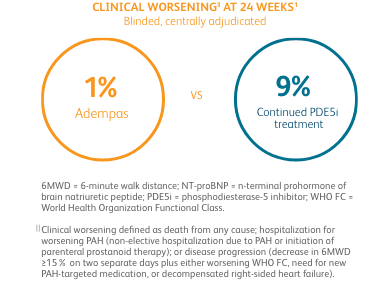
CLINICAL WORSENING ON ADEMPAS VS THOSE CONTINUING TREATMENT WITH A PDE5i1¶
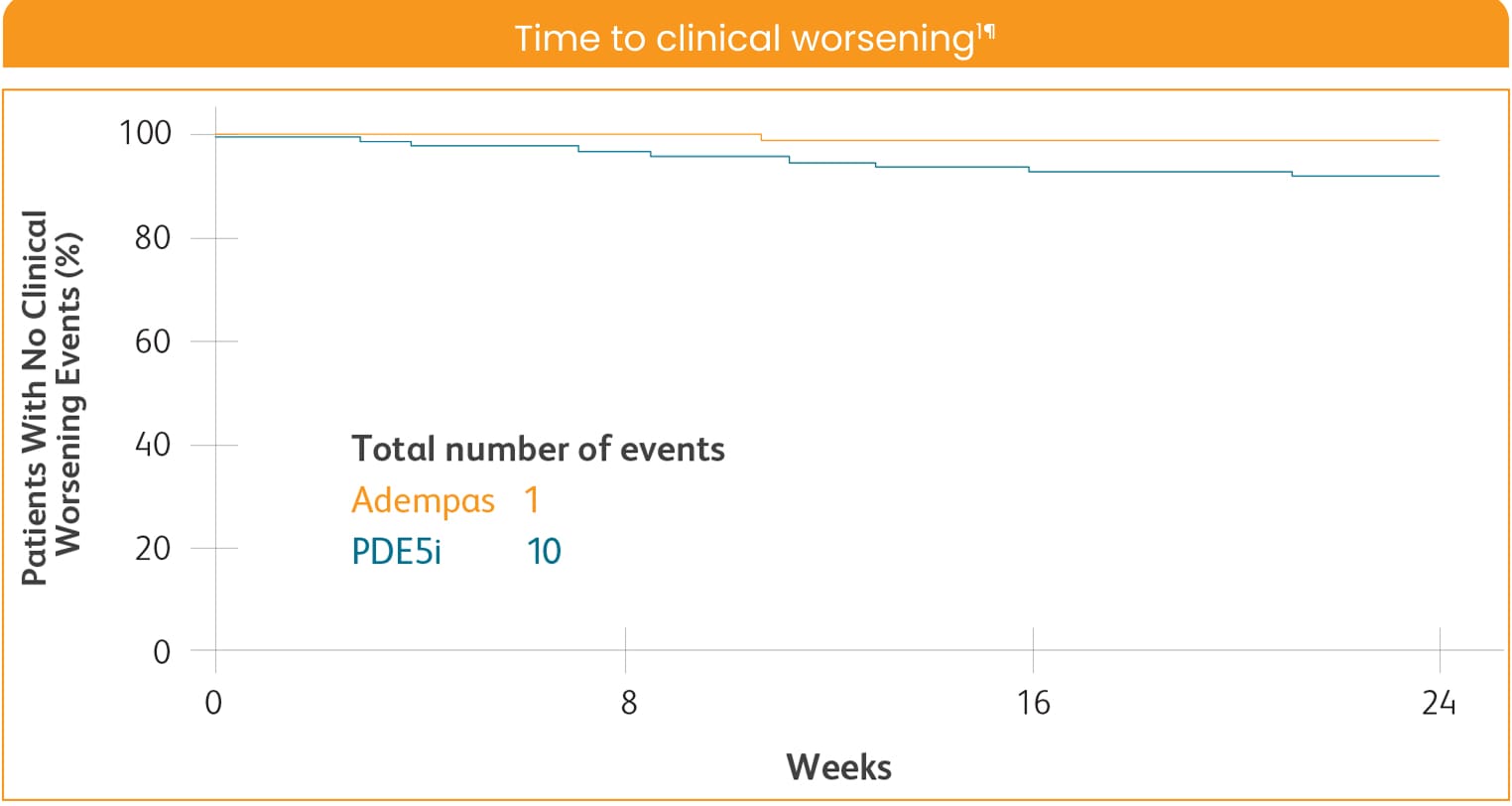
PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor.
¶Clinical worsening defined as death from any cause; hospitalization for worsening PAH (non-elective hospitalization due to PAH or initiation of parenteral prostanoid therapy); or disease progression (decrease in 6MWD ≥15% on two separate days plus either worsening WHO FC, need for new PAH-targeted medication, or decompensated right-sided heart failure).
Results from the REPLACE (Riociguat rEplacing PDE-5i therapy evaLuated Against Continued PDE-5i thErapy) study in adult patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) who were receiving PDE5i therapy and still at intermediate risk1
Adverse events in the REPLACE study1
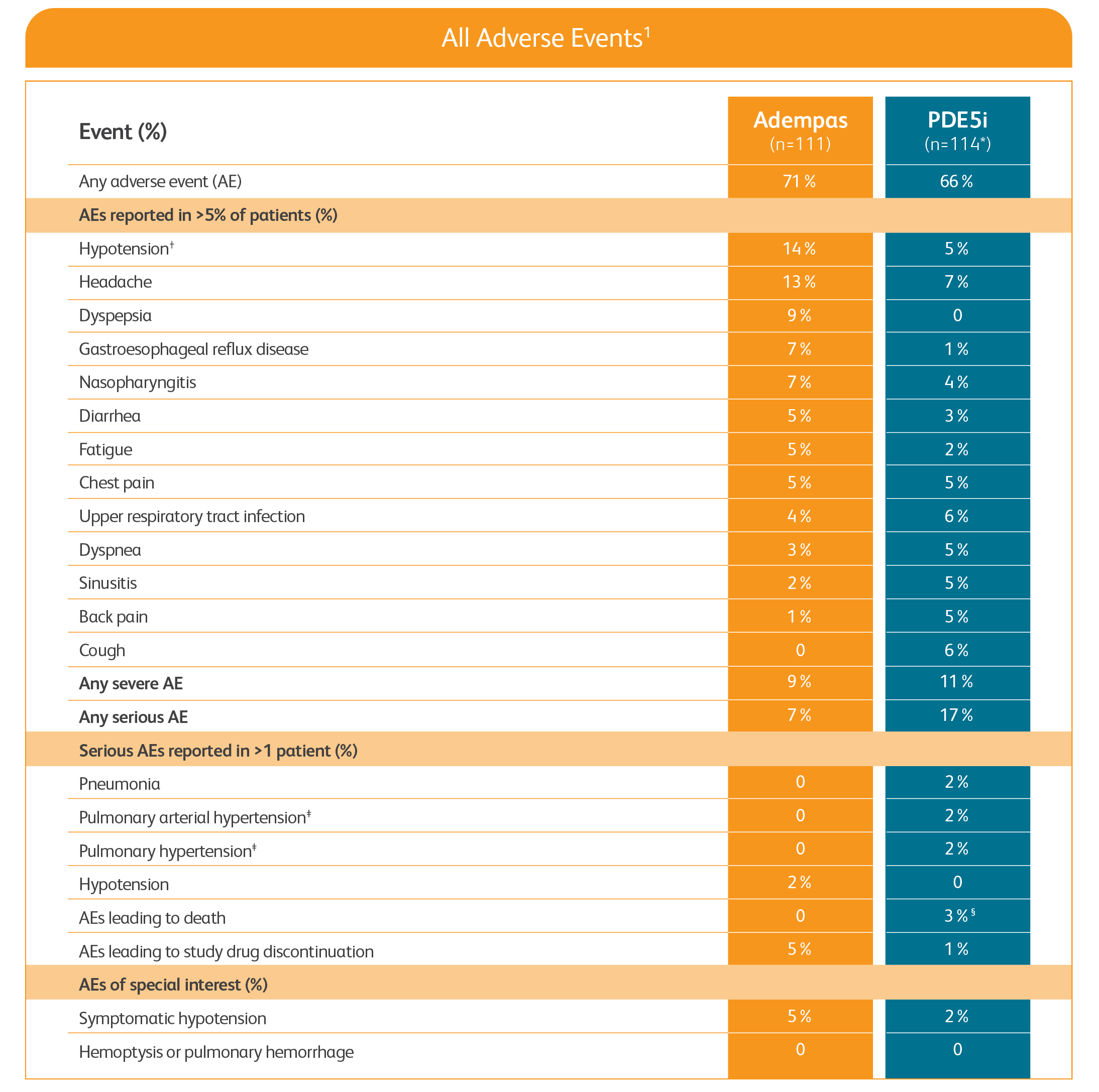
PDE5i = phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor.
One patient was missing components of the primary endpoint at baseline (safety analysis set = 114, full analysis set = 113).
Includes symptomatic and asymptomatic hypotension.
Preferred term for worsening of the condition.
An additional death occurred in the safety follow-up period.
- The safety results are consistent with the known safety profile of Adempas1
- There was no incidence of death in patients transitioned to Adempas during the study or during the 30-day safety follow-up period1
- In patients continuing treatment with PDE5i therapy, 3 deaths were reported during the study period and 1 additional death was reported during the 30-day safety follow-up period1
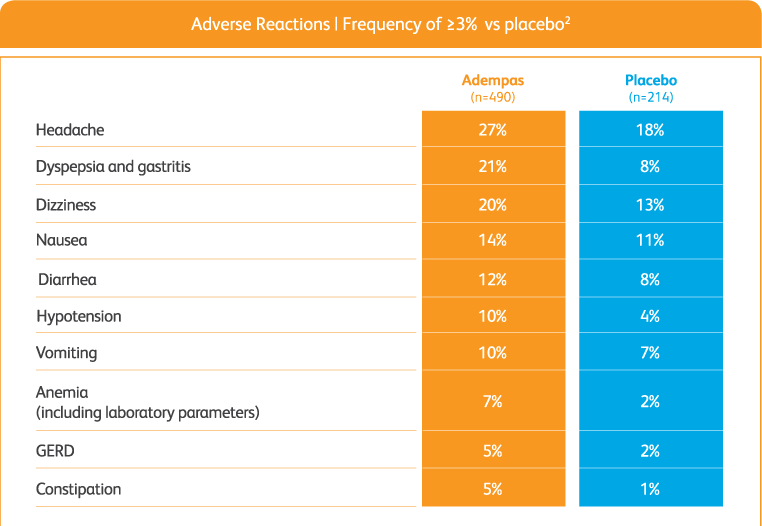
Overall adverse events with adempas2
Adverse reactions (pooled from CHEST-1 and PATENT-1)2
GERD = gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Other events that were seen more frequently in Adempas compared to placebo and potentially related to treatment were2:
- Palpitations
- Nasal congestion
- Epistaxis
- Dysphagia
- Abdominal distension
- Peripheral edema
References:
- Hoeper MM, Al-Hiti H, Benza RL, et al. Switching to riociguat versus maintenance therapy with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (REPLACE): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(6):573-584.
- Adempas Prescribing Information. Whippany, NJ. Bayer Pharmaceuticals Inc., 2023.
- Ghofrani H-A, Galiè N, Grimminger F, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:330-340.
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(38):3618-3731.
- McLaughlin VV, Gaine SP, Howard LS, et al. Treatment goals of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25):D73-D81.