PATENT-1 Study Design
PIVOTAL TRIAL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH PAH (WHO GROUP 1)1
Randomized, double-blind, multinational, placebo-controlled, 12-week, phase 3 study
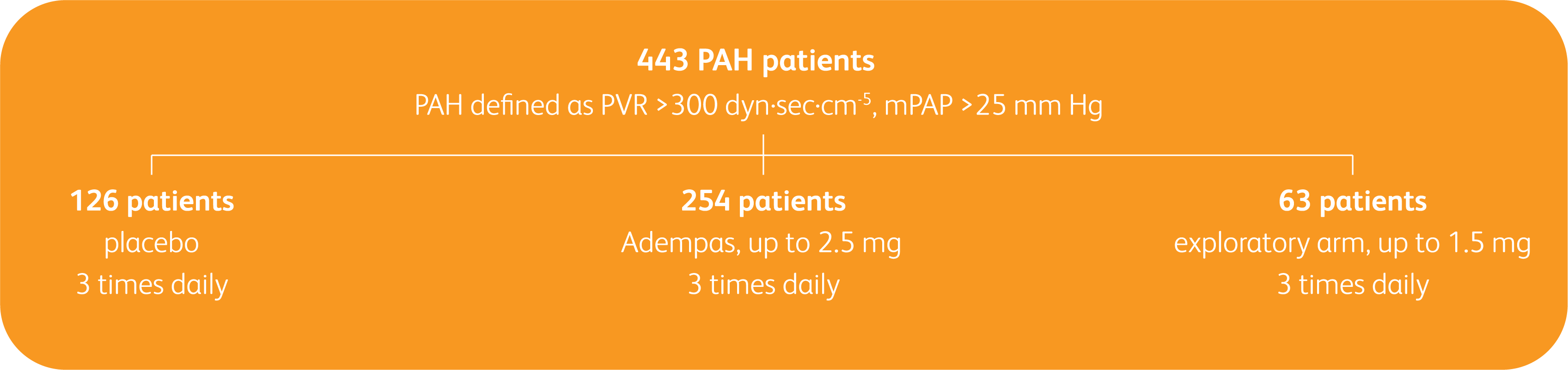
Primary endpoint1
- Change in 6MWD from baseline to Week 12
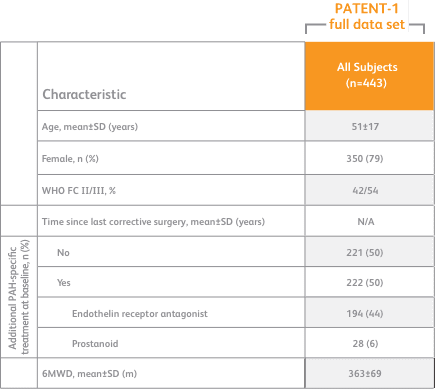
Baseline characteristics1
- Mean age: 51 years (approximately 80% female)
- PAH etiologies: idiopathic (61%), associated with connective tissue disease (25%), congenital heart disease (8%), portal hypertension (3%), familial (2%), or anorexigen or amphetamine use (1%)
- Mean 6MWD was 363 m
- Concomitant medications: oral anticoagulants, diuretics, digitalis, calcium channel blockers, and oxygen were allowed
- Patient population: 50% treatment naïve, 44% pretreated with an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA), and 6% pretreated with a prostacyclin analog (PCA)
- The majority of patients had WHO FC II (42%) or III (54%) at baseline
- Patients with systolic blood pressure <95 mm Hg were excluded
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; mPAP = mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension; PATENT-1 = Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Soluble Guanylate Cyclase-Stimulator Trial; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance; WHO FC = World Health Organization Functional Class.
PATENT-1 Results
IMPROVEMENT IN 6MWD WAS OBSERVED AT 2 WEEKS AND CONTINUED THROUGH 12 WEEKS
SIGNIFICANT IMPROVEMENT IN 6MWD AT WEEK 12
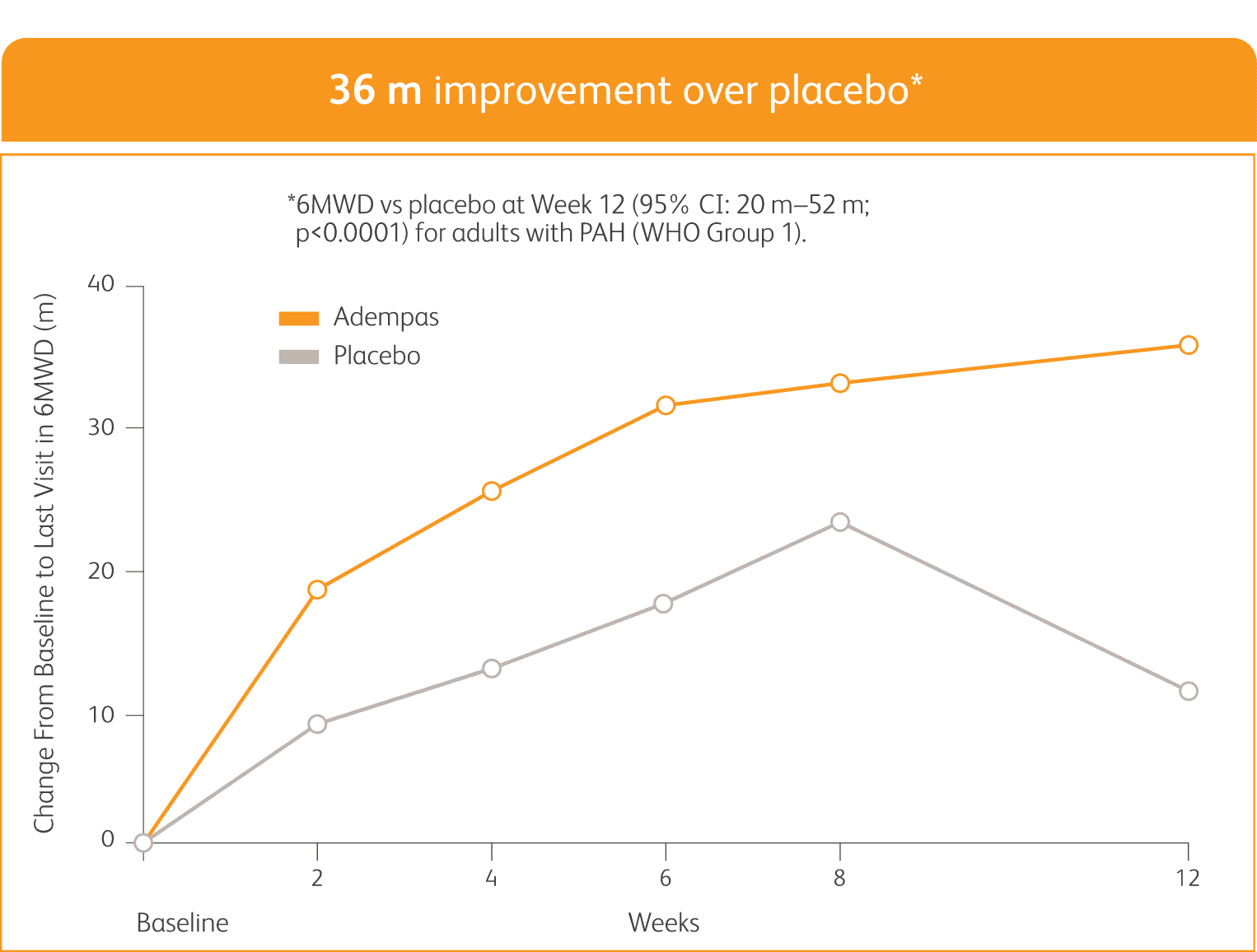
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; CI = confidence interval.
Adempas can be used as monotherapy or in combination
- In WHO FC II and III
- As monotherapy
- In combination with endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs)
- In combination with prostacyclin analogs (PCAs)
50% MORE PATIENTS IMPROVED WHO FC ON ADEMPAS VS PLACEBO
CHANGE IN WHO FC IN THE 12-WEEK PATENT-1 STUDY
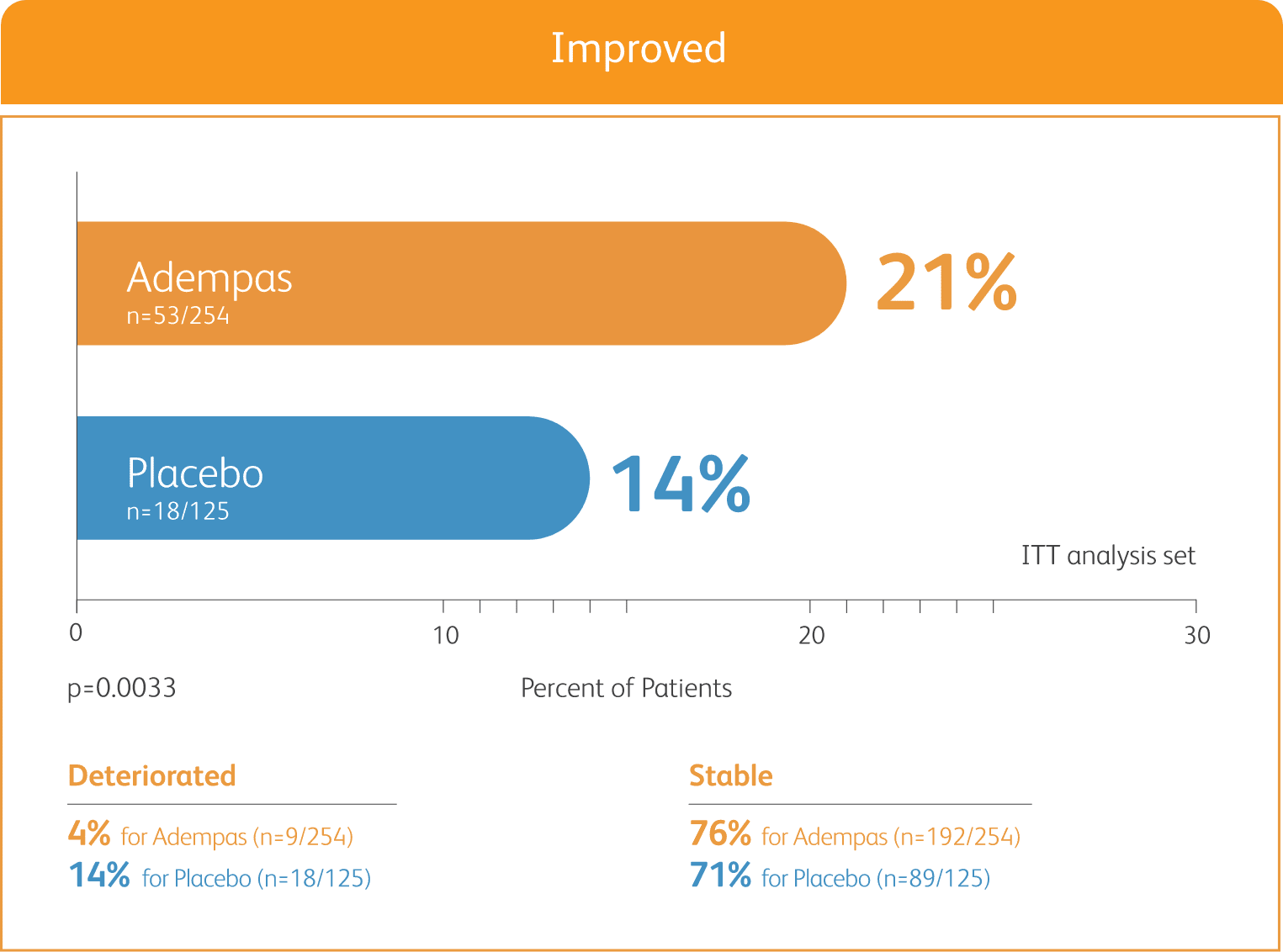
ITT = intention-to-treat.
ADEMPAS SIGNIFICANTLY DELAYED TIME TO CLINICAL WORSENING†
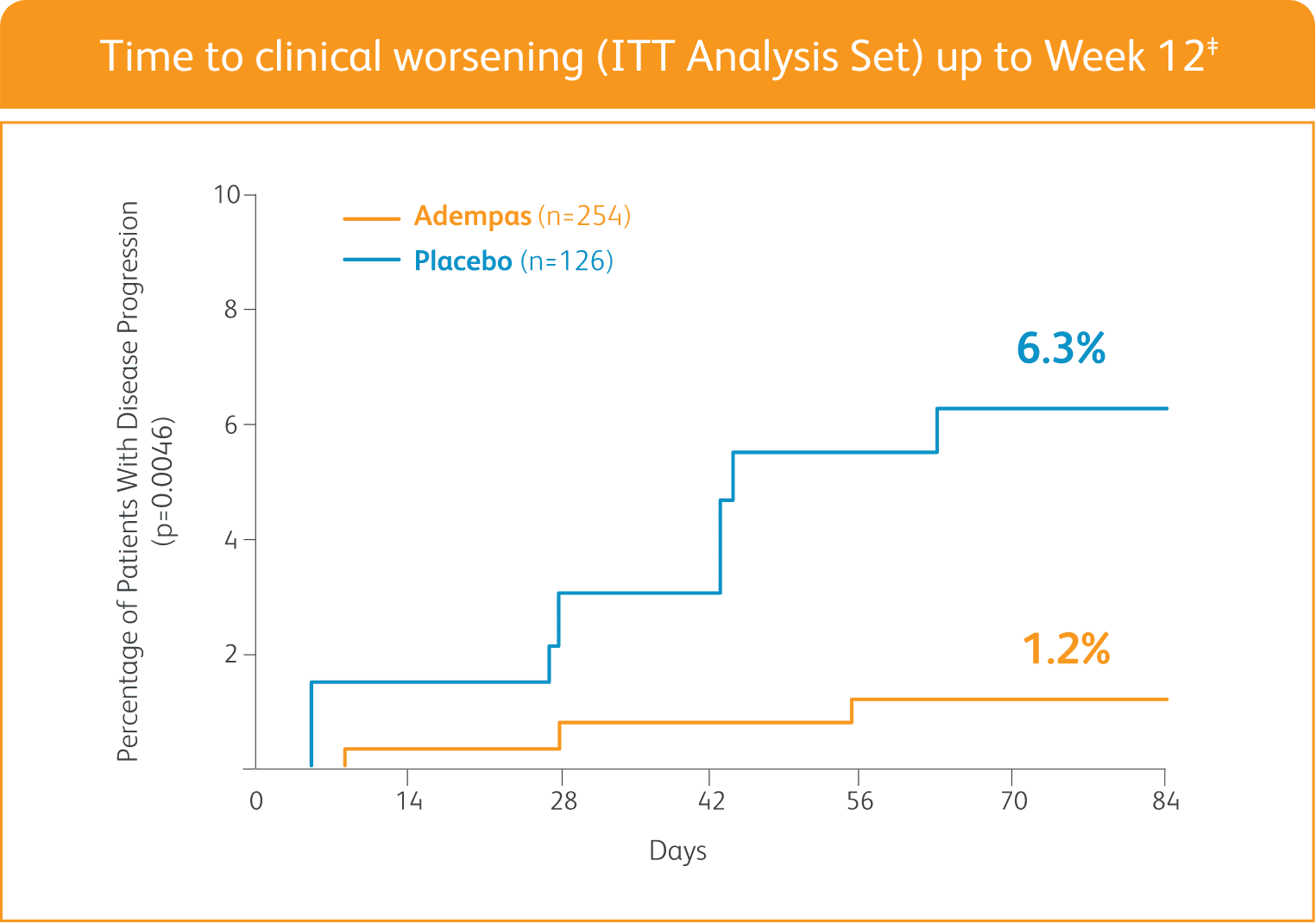
†Time to clinical worsening was a combined endpoint defined as death (all-cause mortality), heart/lung transplantation, atrial septostomy, hospitalization due to persistent worsening of pulmonary hypertension, start of new PAH-specific treatment, persistent decrease in 6MWD, and persistent worsening of WHO FC.
‡The Kaplan-Meier plot of time to clinical worsening is presented in the figure above. Patients treated with Adempas experienced a significant delay in time to clinical worsening vs placebo-treated patients (p=0.0046; stratified log-rank test). Significantly fewer events of clinical worsening up to Week 12 (last visit) were observed in patients treated with Adempas (1.2%) compared to placebo (6.3%) (p=0.0285, Mantel-Haenszel estimate).
ADEMPAS IMPROVED PVR AND NT-proBNP AT WEEK 12
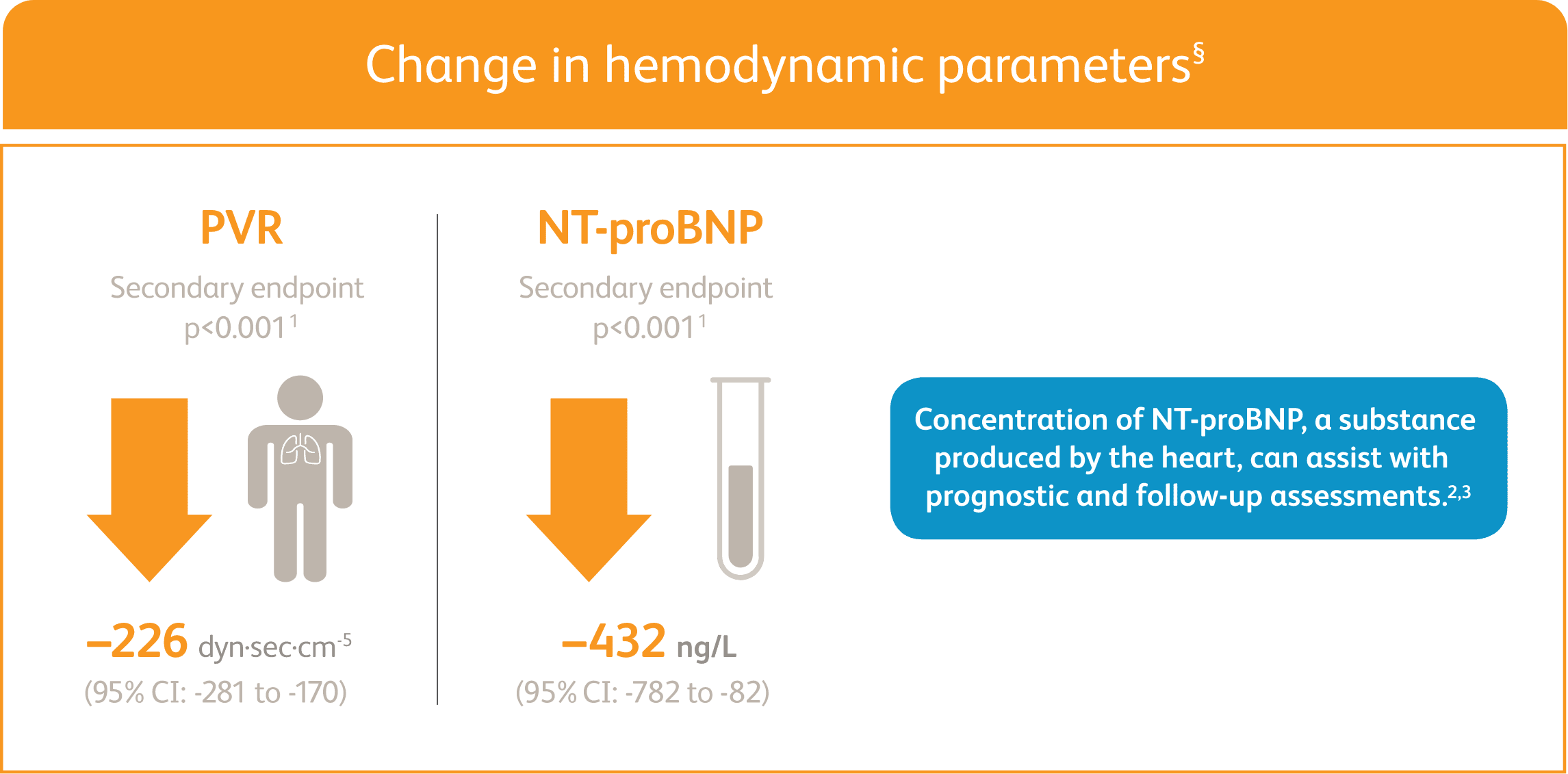
Right heart catheterization was performed at the beginning and end of the study period in 339 patients.
NT-proBNP = n-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance.
§Placebo-adjusted mean change from baseline.
PATENT-1 Study Design
PATENT-1: A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTINATIONAL, MULTICENTER, PLACEBO-CONTROLLED PHASE 3 STUDY
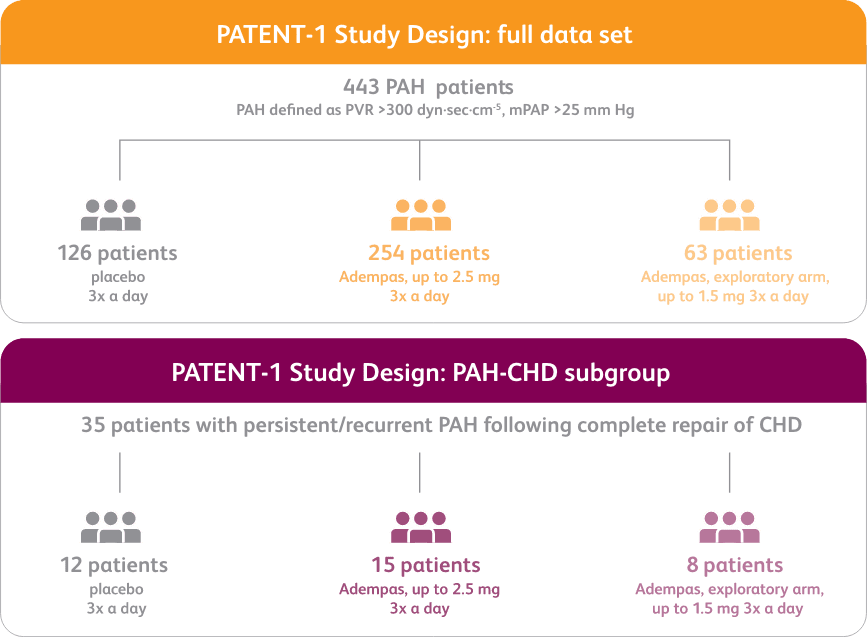
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS1,2
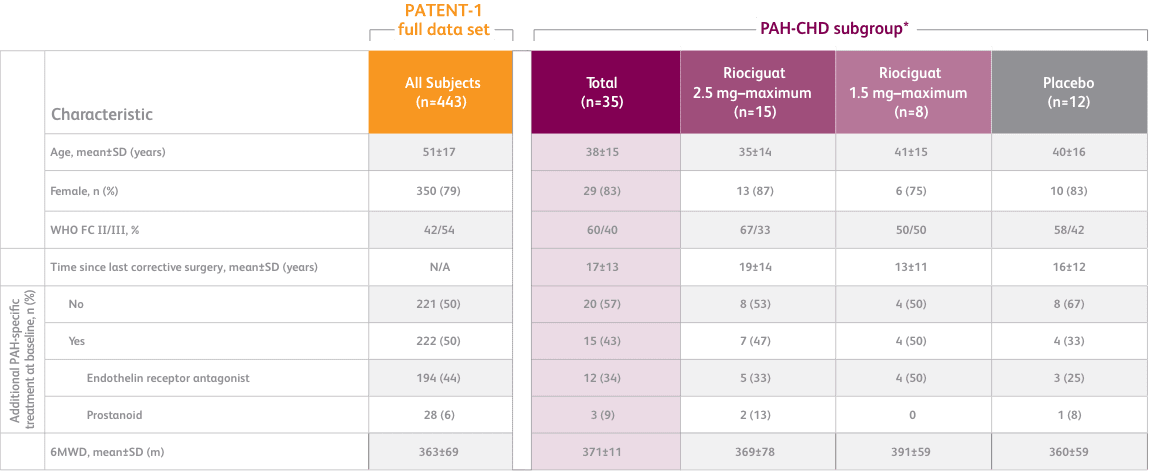
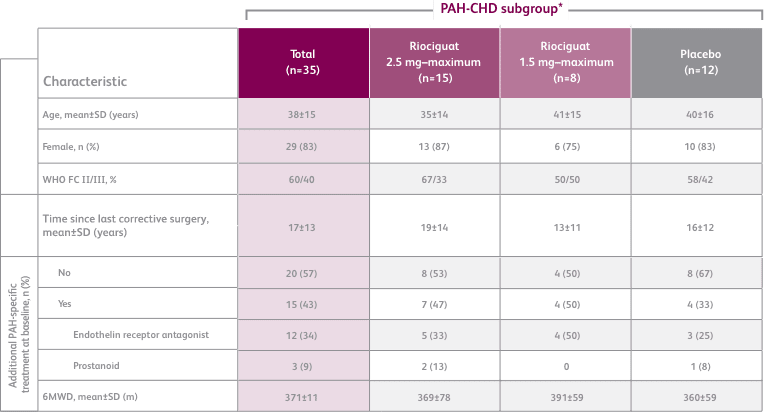
- Efficacy data were only measured for the Adempas 2.5 and placebo arms
- Concomitant medications: oral anticoagulants, diuretics, digitalis, calcium channel blockers, and oxygen were allowed
- Patients with systolic blood pressure <95 mm HG were excluded
- PATENT-1 PAH etiologies: idiopathic (61%), associated with connective tissue disease (25%), congenital heart disease (8%), portal hypertension (3%), familial (2%), or anorexigen or amphetamine use (1%)
- CHD subtypes include corrected atrial septal defect, corrected ventricular septal defect, corrected persistent ductus arteriosus, and not specified1
6MWD = 6-minute walk distance; SD = standard deviation; WHO FC = World Health Organization Functional Class.
*exploratory subgroup analysis.
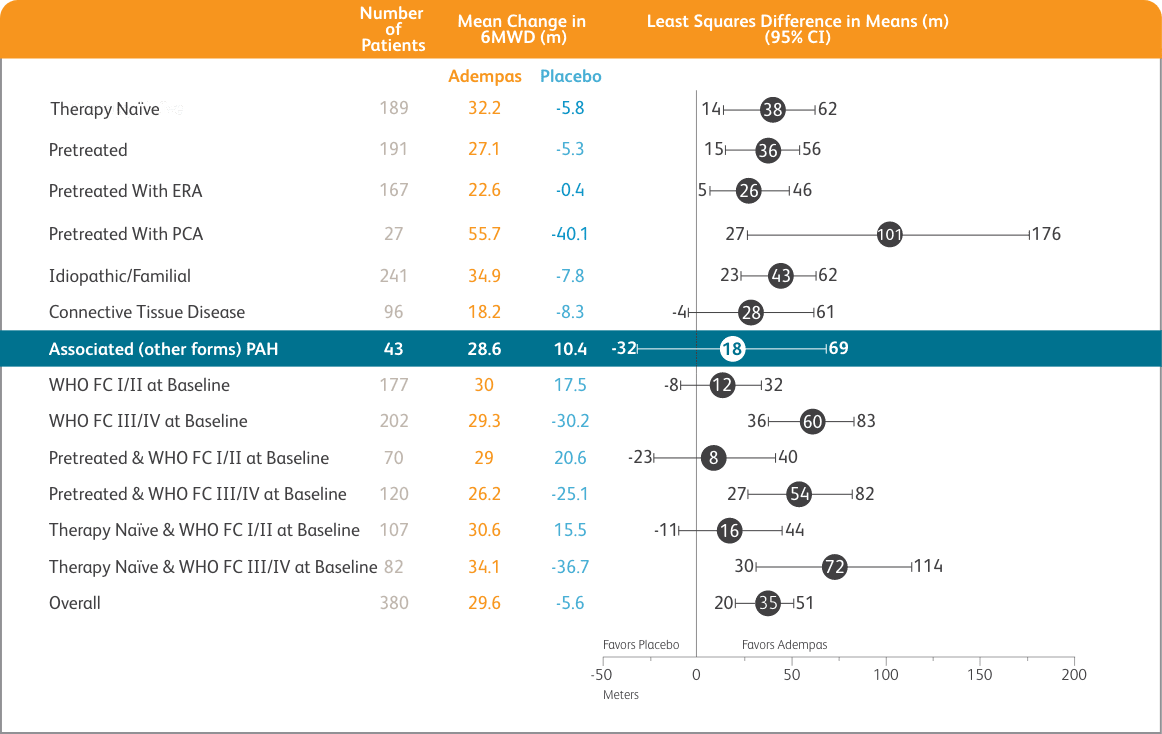
PATENT-1 MEAN TREATMENT DIFFERENCE IN CHANGE FROM BASELINE TO LAST VISIT IN 6-MINUTE WALK DISTANCE (METER) BY PRESPECIFIED SUBGROUPS
PATENT-1 Results in the CHD Subgroup
Data from the PAH-CHD subgroup analysis are exploratory, as PATENT-1 was not designed to show statistically significant differences in subgroup populations. The primary efficacy analysis was performed on data from the modified intent-to-treat population (all patients who were randomized and received one or more doses of the study drug). The data presented here are observed values and are analyzed descriptively; observed values were used due to the small sample size and the retrospective, exploratory nature of the analyses. The low patient numbers in the PAH-CHD subgroup should be taken into consideration when interpreting the data. Time to clinical worsening was not evaluated in the PAH-CHD subgroup within the PATENT-1 study.
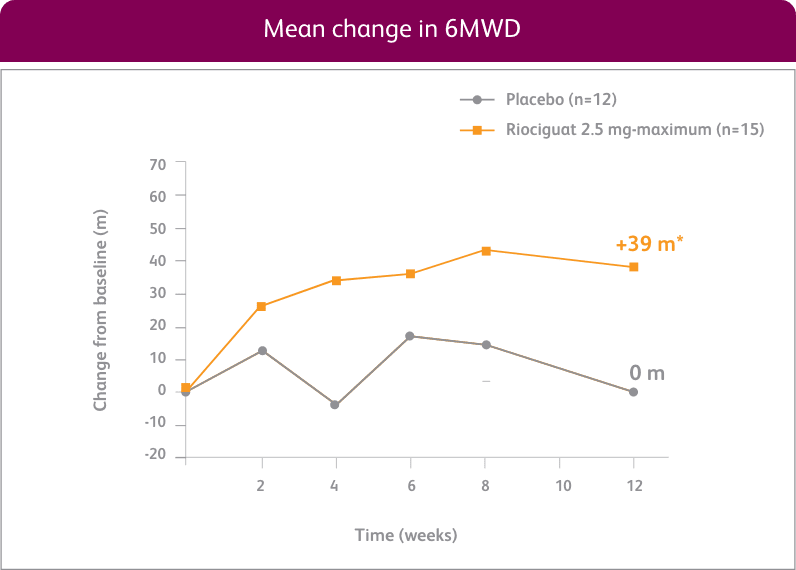
CHANGE IN 6MWD FROM BASELINE AT WEEK 121
EXPLORATORY POST HOC SUBGROUP ANALYSIS
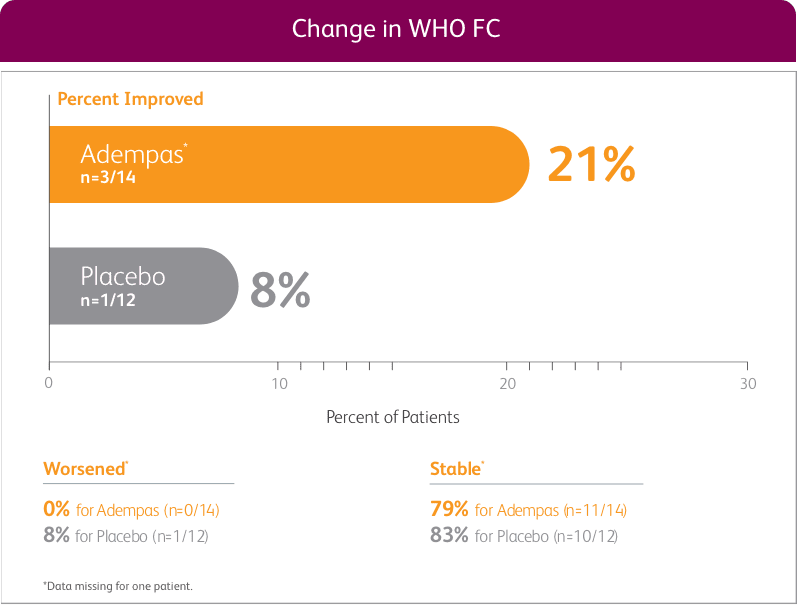
CHANGE IN WHO FC FROM BASELINE AT WEEK 121
EXPLORATORY POST HOC SUBGROUP ANALYSIS
PVR AND NT-proBNP VALUES AT WEEK 121
EXPLORATORY POST HOC SUBGROUP ANALYSIS
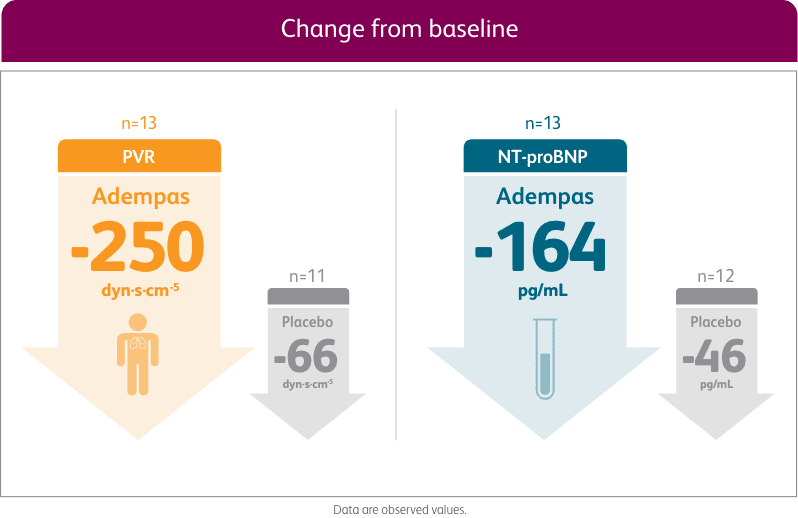
PAH-CHD IS A FORM OF ASSOCIATED PAH (WHO GROUP 1)1
- CHD (congenital heart disease) refers to a range of cardiac defects resulting from structural abnormalities of the heart or blood vessels that develop before birth and can result in impaired cardiac blood flow3,4
— PAH-CHD is the second most common form of associated PAH in adults1,5,6 - 5-10% of adult patients with CHD will develop PAH6
- PAH-CHD in adults is challenging to manage, due to the heterogeneous nature of the disease and an increase in comorbidities
References:
- Ghofrani HA, Galiè N, Grimminger F, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:330-340.
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(1):67-119.
- McLaughlin VV, Gaine SP, Howard LS, et al. Treatment goals of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25):D73-D81.
References:
- Rosenkranz S, Ghofrani H-A, Beghetti M, et al. Riociguat for pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease. Heart. 2015;101(22):1792-1799.
- Ghofrani HA, Galiè N, Grimminger F, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:330-340.
- Zaidi S, Brueckner M. Genetics and genomics of congenital heart disease. Circ Res. 2017;120(6):923-940.
- US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC website. What are congenital heart defects? Published January 24, 2022. Accessed June 10, 2022.
https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/facts.html - Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2009;34(6):1219-1263.
- Opotowsky AR. Clinical evaluation and management of pulmonary hypertension in the adult with congenital heart disease. Circ. 2015;131(2):200-210.



